Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. In high-income countries, most people recover within two to three weeks, and the mortality rate is low. In developing countries, however, the mortality rate is between 3 and 15%, and can be as high as 20% in more vulnerable people. Complications such as acute respiratory infection, diarrhea, dehydration, or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) are usually the cause.
Measles is spread by droplets from the nose, mouth or throat of infected people, which are spread by coughing, sneezing and breathing.
the cost of vaccinating one child against measles
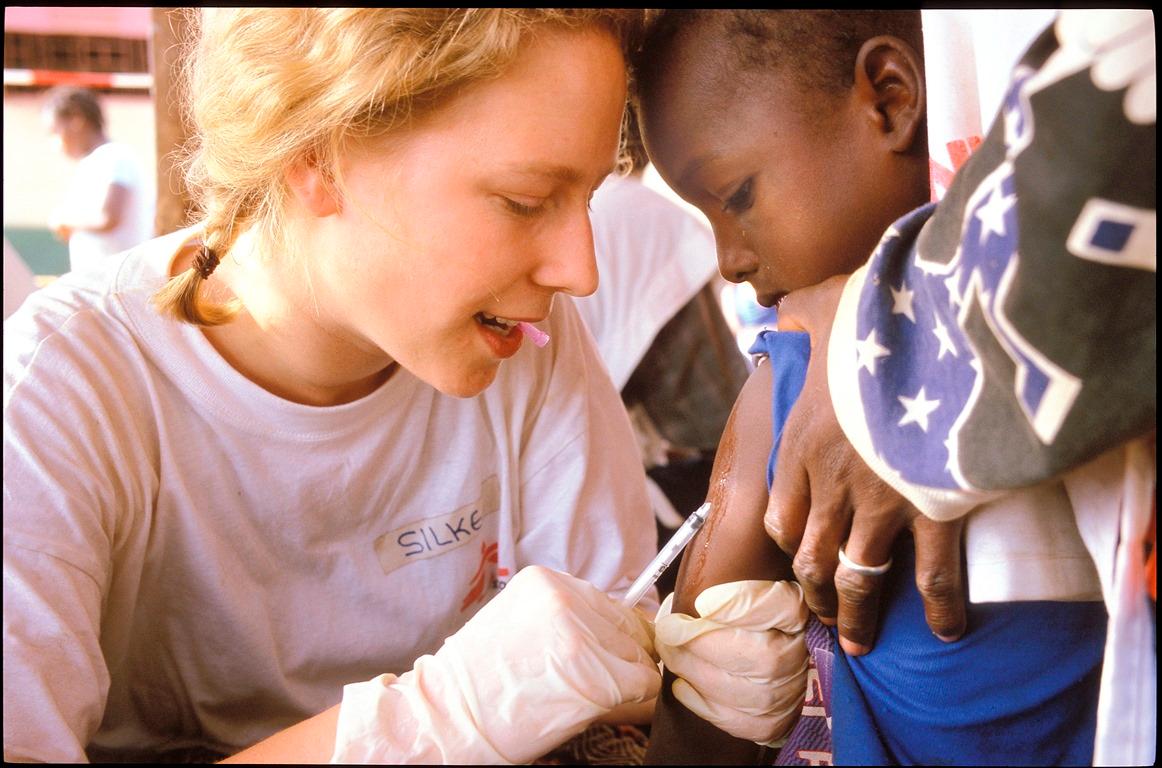
people vaccinated by MSF in 2023 in response to outbreaks
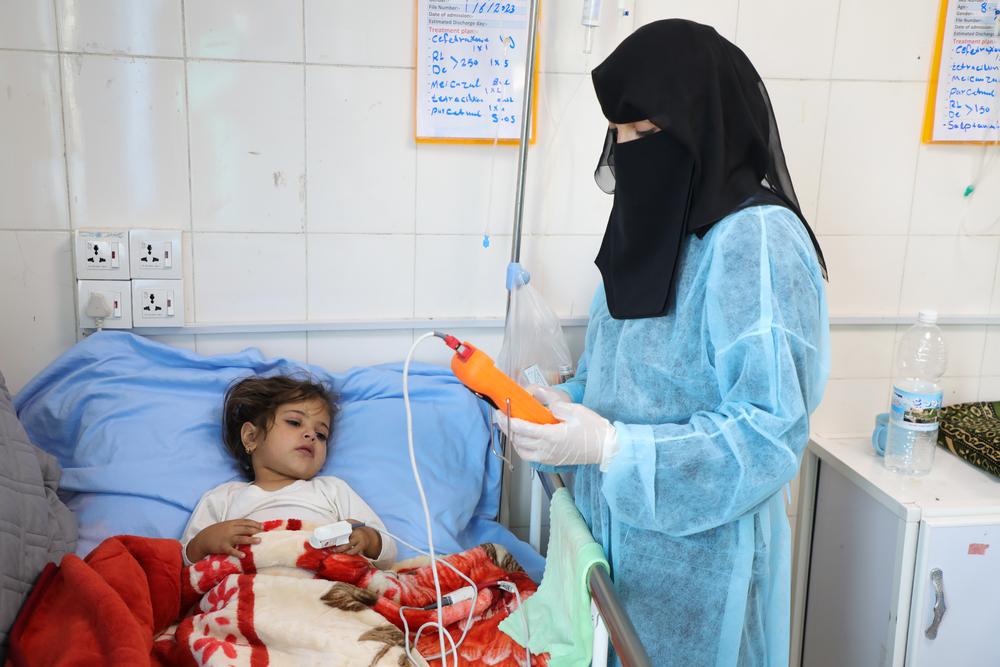
people treated for measles by MSF in 2023
Symptoms
Symptoms appear eight to 13 days after exposure to the virus and include a runny nose, cough, eye infections, rash and high fever.
Treatments
There is no specific treatment: patients are isolated and given vitamin A, and complications such as eye problems, stomatitis (viral infection of the mouth), dehydration, protein deficiencies and respiratory infections are treated.
There is an effective and affordable measles vaccine, and widespread vaccination campaigns have significantly reduced measles-related morbidity and mortality. However, many people remain vulnerable to the disease, particularly in countries with weak health systems, frequent outbreaks, and limited access to health services.